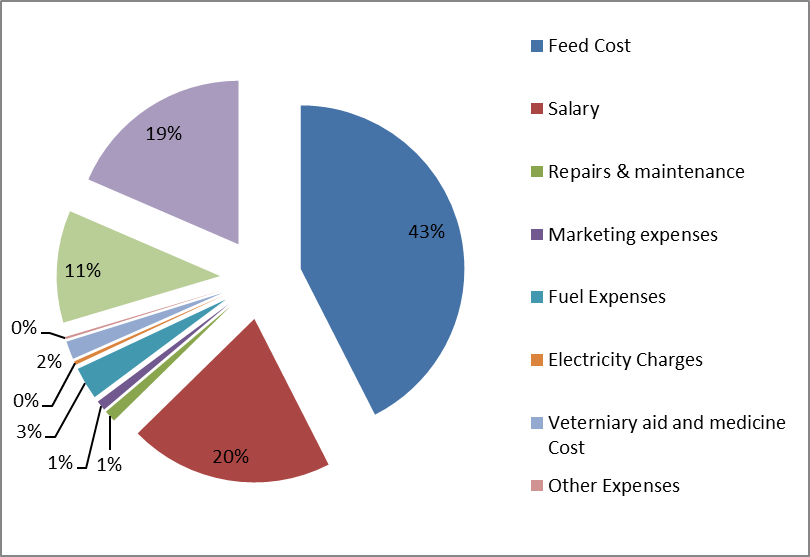
Feed Cost Management
Feed cost management is one of the most essential aspects of ensuring the success of a dairy farm. Hence, all measures for reducing feed costs must be monitored and regulated. As per data collected from some farms in Kerala, feed costs consume 43% of the total cost, and feeding expenses may reach up to 60% of the overall cost, depending on the resources used. It is important to promote in-house feeding methods such as green fodder cultivation and the use of cheaper substitutes for compound feed to ensure the profitability of the project.
Labour Management
Labour is the second-largest cost component that must be monitored for the smooth functioning of the project. Studies suggest that one labourer is required to look after 10 cows. Hence, maintaining a 1:10 ratio is crucial for cost management and profitability. In Kerala, wage rates are typically higher compared to other states in the country. Therefore, a strict labour employment ratio should be maintained to ensure the profitability of the cattle farm.
Breeding Management
Proper breeding management depends on various factors, including maintaining a healthy ratio of milking and non-milking cows and ensuring reproductive efficiency. In Kerala, the typical milking-to-non-milking cow ratio is 80:20, meaning that for every eight milking cows, two non-milking cows are recommended. If the ratio falls below 1:1, farm profitability is significantly hampered.
Reproductive efficiency is influenced by genetic and non-genetic factors. Non-genetic factors such as climate, nutrition, and poor management play a major role in breeding outcomes. It is essential for farm owners and management staff to have a thorough understanding of breeding management. Factors such as fertilization rates, the number of ova, and embryonic mortality are all crucial for effective breeding.
Breeding efficiency can be significantly improved by reducing the interval between successive pregnancies and lowering the age of first breeding. If artificial insemination is not used, there must be a proper cow-to-bull ratio for effective breeding management. A general guideline suggests a 1:25 bull-to-cow ratio, which may vary from 1:15 to 1:30, depending on the age, breed, and pasture size of the bulls. However, according to the latest data, the average bull-to-cow ratio in Indian farms is 1:4, which significantly hampers the profitability of cattle farms.
(This article is derived from the feasibility study conducted by us for setting up a profitable cattle farm )
